Terms You Need to Know:

Christopher Columbus arriving in the America. Image Source
Abolition: The ending of a law, a system or an institution. During the 19th century, the Abolition of Slavery Act ‘officially’ ended slavery in 1834.
Cartographer: A person who draws or makes maps.
Colonialism: The practice by which a powerful country controls another country or civilization.
Colonization: The act of taking control of an area or a country that is not your own, especially using force, and sending people from your own country to live there.
Colony: A country or an area that is governed by people from another, and often more powerful, country.
Conquest: The act of taking control of a country, city, etc. by force.
Conquistador: One of the Spanish people who took control of Mexico and Peru by force in the 16th century.
Emancipation: The act of freeing somebody, especially from legal, political or social controls that limit what they can do. For example, the emancipation of people enslaved (slaves).
Indigenous: Belonging to a particular place rather than coming to it from somewhere else. A synonym: native.
Missionaries: A person who is sent to a foreign country to teach people about religion.
Plantation: A large area of land, especially in a hot country, where crops such as coffee, sugar, rubber, etc. are grown.
Settlement: A place where people have come to live and make their homes, especially where few or no people lived before.
Slavery: This refers to the state of one person being sold for monetary and or other gain by slave-owners. This could also refer to the state of owning a person who is sold/bought for profit and/or labour.
Smallpox: A serious disease that caused a high temperature, left permanent marks on the skin and often caused death.
Historical examples of Smallpox:[1]
- 6th Century – Increased trade with China and Korea introduces smallpox into Japan.
- 7th Century – Arab expansion spreads smallpox into northern Africa, Spain, and Portugal.
- 11th Century – Crusades further spread smallpox in Europe.
- 15th Century – Portuguese occupation introduces smallpox into part of western Africa.
- 16th Century – European colonization and the African slave trade import smallpox into the Caribbean and Central and South America.
- 17th Century – European colonization imports smallpox into North America.
- 18th Century – Exploration by Great Britain introduces smallpox into Australia.
Trading Post: A general store established by a trader in an unsettled or thinly populated region.[2]
Triangular Trade: Triangular trade refers to a three-legged journey where traders buy/sell various goods, making a profit on each leg. During the 16th century various European travelers such as the Portuguese and Spanish took part in the ‘Triangular Slave Trade’.
Triangular Slave Trade: This journey usually started from the coast of Europe where the ships were filled with various goods such as iron, wine, guns and textiles which were transported to various ports on the North-Western coast of Africa. These goods were then exchanged for enslaved indigenous people from Africa and transported to the Caribbean islands of the Americas and sold to plantation owners and forced into manual labour. In exchange for these slaves, the plantation owners ‘sold’ goods such as sugar, tobacco and coffee which was then transported back to the European coast to be sold for a profit.
Middle Passage: The ‘middle passage’ refers to the Journey between Africa and America across the Atlantic Ocean (the middle passage of the triangular trade) where thousands of enslaved people died onboard the ships they were ‘stored’ in.
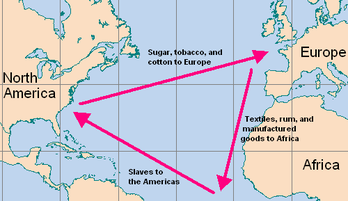
An image portraying the ‘Triangular Slave Trade’ that was a result of European expansion and conquest.Image Source
This content was originally produced for the SAHO classroom by
Ilse Brookes, Amber Fox-Martin & Simone van der Colff
[1] Author Unknown, “Smallpox: History of Smallpox,” Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [online], Available at https://www.cdc.gov/smallpox/history/history.html (Accessed on 29 July 2020).
[2] Author Unknown, “English Dictionary,” Reverso Dictionary [online], Available at https://dictionary.reverso.net/english-definition/trading+station (Accessed on 29 July 2020).